According to commit4fitness, the Dominican Republic is a Caribbean nation located on the island of Hispaniola. It has an open and liberal economy with a focus on services, industry and tourism. The services sector includes banking and finance, telecommunications, transport and logistics as well as retail. The industrial sector produces a range of products including apparel, chemicals and food products which are used both locally and exported. In addition, the tourism industry is also well developed with visitors from all around the world coming to experience its vibrant culture and attractions. Furthermore, there are several international companies operating in the Dominican Republic such as American Airlines or Procter & Gamble who have taken advantage of the country’s favorable business environment.
According to abbreviationfinder, DR is the 2 letter abbreviation for the country of Dominican Republic.
In 2014, the Dominican Republic was among the countries of Latin America and the Caribbean with the highest GDP growth, according to figures from CEPAL. In the years 1991-2013, the country experienced an average 5.5% increase in GDP, according to the World Bank. Despite this, poverty has risen sharply, especially in the early 2000s, according to the same source.
In the 1960s and 1970s, the country was well-paid for sugar, and economic growth was among the strongest in the Caribbean. Weak markets and falling sugar prices have weakened the country’s economy since 1980. Since 1990, the economy has also been hit hard by an unstable electricity supply. There is high unemployment and underemployment, and unemployment is high.
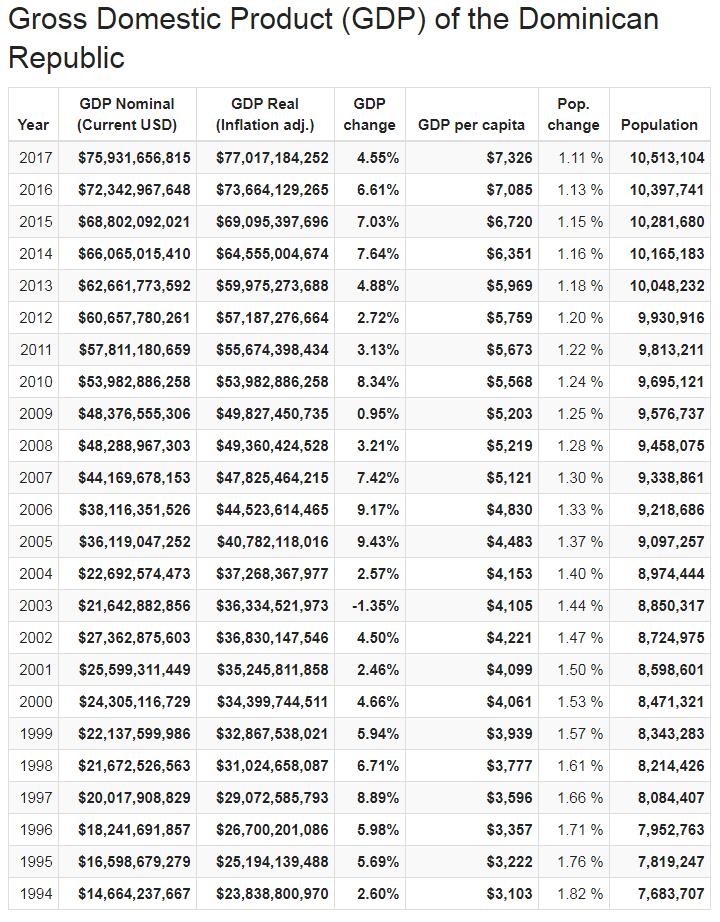
The country’s main sources of income have evolved into an ever-growing tourism industry as well as repatriation of foreign currency from exiled Dominicans. A heavy foreign debt has forced the country to seek debt negotiations with the International Monetary Fund. In 2002, the gross domestic product (GDP) was estimated at USD 6000 per capita.
The tourism industry is a focus area and in recent years there has been a significant expansion of hotels, improvement of roads and more. The best developed places are the Puerto Plata and Sosua area, Punta Cana and the Samaná Peninsula. In 2014, the country was visited by 5,141,377 tourists, according to figures from the Dominican Central Bank, which is a new record.
Agriculture
Agriculture used to be the most important trade route and now comprises 12% of GDP (2002) and employs approx. 15% of the working population. Of the land area, 30% is cultivated. The Ciba Valley in the central northern part of the country has the most fertile soil. However, sugar cane, which is the most important export product from agriculture, is grown mostly on large plantations in the eastern part of the country. Until 1984, sugar production produced large export revenues to the country. Since then, changing import needs in the United States have hit sugar exports hard. In the first half of the 1990s, both production volume and export revenue declined. Sugar cane production was 4.8 million tonnes in 2002 and the export value of raw sugar and sugar products accounted for only 7% of the country’s total export value.
Other export crops are coffee, cocoa and tobacco, which are mainly grown in the Cibao Valley. However, most of the farmers run low-yield self-storage farms. The production of the most important nutritional products (including corn, rice, cassava, yams, sweet potatoes) is often not sufficient to meet local needs.
Livestock farming on a commercial basis is particularly concentrated in the north of the country and in the lowlands in the east, with the production of beef for domestic consumption. Milk production takes place substantially in the south and in Sousa on the north coast. There is a modest coastal fishery.
Energy
Energy consumption is low. Most of the energy comes from thermal power based on imported oil. The country has been affected since the early 1990s by an energy crisis with unstable power supply up to 20 hours per day. This is due to a combination of old and poorly run energy plants as well as lack of heating oil, which in turn is due to a lack of foreign currency. In addition, hydropower plants’ production has been affected by low water levels. A new hydropower plant; Monción in Santiago Rodríguez, opened in 2001.
Industry and mining
In 2001, the industry (including mining and more) accounted for 33% of gross domestic product and 21% of employment. A large part of industrial capital is in American hands. The industrial activities are to a large extent based on refining sugar and processing other primary agricultural products, including the large production of beer and cigarettes. Large cement production. Most of the industry is concentrated in the capital Santo Domingo.
Several economic frisons have been created with special incentives such as low taxes and fees to attract foreign production establishments. Manufacturing finished products for the North American market is an important part of this business.
It is estimated that the country has approx. 10% of the occurrence of ferric nickel in the world, and in 2000 ferronicle accounted for approx. 25% of export revenue. However, fluctuations in prices and demand in the world market have led to mining cessation of periods. Some gold and silver are also extracted. An earlier significant bauxite recovery has now completely ceased.
Foreign Trade
According to Countryaah, the main export goods are iron and steel, sugar and sugar-based products. Petroleum, petroleum products and food are the most important import goods. Major trading partners are the United States, Haiti, Venezuela, Mexico, the Netherlands, Belgium and Japan. The country receives large shipments of currency from persons residing abroad.
Transport and Communications
The road network is relatively well developed. The main roads extend from Santo Domingo to the north, east and west and connect the capital with Port-au-Prince in Haiti, among others.
There are railways, but these are mainly run by the sugar companies, in connection with sugar production.
International airports can be found at Santo Domingo (Aeropuerto Internacional de las Americas), Santiago de los Caballeros (Aeropuerto Internacional del Cibao), Punta Cana (Aeropuerto Internacional de Punta Cana), SAmaná (Aeropuerto Internacional Samaná El Catey) and Puerto Plata. Santo Domingo, with approx. 80% of exports are the largest port city; Puerto Plata is the most important port on the north coast.